What is Cloud Computing? Everything You Need to Know | Connect Infosoft

Book Service: https://www.connectinfosoft.com/cloud-computing-development-services/
The concept of the cloud is no longer entirely unknown. It's a term used so frequently in digital transformation and modern technology that we've accepted that the cloud will be a part of everyday life - even if the implications of the cloud shift aren't completely understood. However, failing to comprehend cloud architecture and the benefits it provides means that we are taking this critical technology for granted.
And a greater understanding of cloud computing is required to appreciate the cloud: What exactly is it, and how does it work?
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the way to share computer resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics via the internet. Instead of hosting and managing these resources locally or on-premises, cloud computing enables users to access and utilize them remotely through a network connection, typically the internet.3
Characteristics Of Cloud Computing:
On-Demand Self-Service:
Users can provision and access computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, or applications, on-demand without requiring human intervention from the service provider.
Broad Network Access:
Cloud services are accessible over the network and can be accessed by users using various devices, including laptops, smartphones, or tablets, from anywhere with an internet connection.
Resource Pooling:
Cloud providers pool and allocate computing resources dynamically across multiple users, enabling efficient utilization and scalability. Users typically share the underlying infrastructure, while their specific resources and data remain isolated and secure.
Rapid Elasticity:
Cloud resources can be scaled up or down quickly and automatically based on demand. This allows users to adjust their resource allocation to match their needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Measured Service:
Cloud computing resources are often provided and billed based on usage, offering a pay-as-you-go model. Users can monitor and track their resource consumption, allowing for cost optimization and accountability.
Cloud Computing Has The Following Advantages:
Scalability:
Cloud services can scale dynamically to accommodate varying workloads and user demands. Resources can be easily allocated or de-allocated, allowing businesses to quickly respond to changing needs without significant upfront investments.
Cost Efficiency:
Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure investments and provides a flexible pay-as-you-go model. Users pay only for the resources they consume, reducing capital expenditures and enabling cost optimization.
Reliability and Availability:
Cloud providers typically offer robust infrastructure and redundancy measures, ensuring high availability and minimizing downtime. Data backups, disaster recovery, and automatic failover mechanisms are often built into cloud services.
Global Accessibility and Collaboration:
Cloud computing enables easy access to resources and applications from anywhere in the world, fostering collaboration and remote work. It allows geographically distributed teams to work together seamlessly.
Innovation and Agility:
Cloud computing provides a platform for rapid development and deployment of applications and services. It allows businesses to experiment, iterate, and innovate more quickly, accelerating time-to-market.
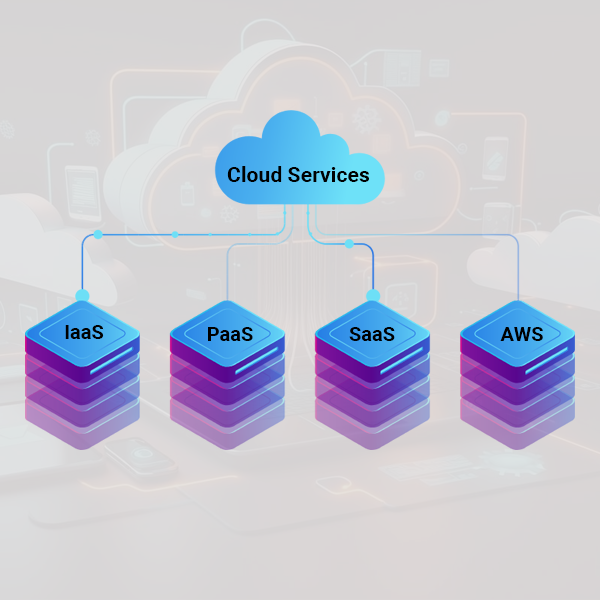
Types Of Cloud Services:
Cloud services can be categorized into three main types, known as the cloud service models or cloud computing models. These models define the level of control and responsibility that the cloud provider and the user have over the underlying infrastructure and services. Cloud services are classified into three types:
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service delivers virtualized computer resources to users via the internet. With IaaS, users have control over the operating systems, applications, and storage, while the underlying infrastructure, including servers, networking, and data centers, is managed by the cloud provider. Users can scale resources up or down based on their needs, allowing for flexibility and cost optimization. Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Compute Engine are examples of IaaS providers.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service offers a higher level of abstraction, providing users with a platform on which they can develop, deploy, and manage applications. PaaS removes the need for users to manage the underlying infrastructure, operating systems, and runtime environments, allowing them to focus on application development and deployment. The cloud provider takes care of tasks such as hardware and software maintenance, scalability, and security. Heroku, Google App Engine, and Microsoft Azure App Service are examples of PaaS providers.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a Service delivers ready-to-use applications over the internet. With SaaS, users access and use software applications hosted on the cloud provider's infrastructure. The cloud provider manages all aspects of the application, including infrastructure, software updates, security, and maintenance. Users typically access the application through a web browser or a thin client. Examples of SaaS applications include Salesforce, Google Workspace, Dropbox, and Microsoft Office 365.
Types Of Cloud Deployments:
Cloud deployments can be categorized into different types based on the level of accessibility, ownership, and infrastructure configuration. The three main types of cloud deployments are:
1. Public Cloud:
Public cloud deployments involve hosting services and infrastructure on shared resources provided by third-party cloud service providers. These resources are accessible to the public over the internet. In a public cloud deployment, multiple organizations or individuals share the same infrastructure, and the cloud provider handles the management, maintenance, and security of the underlying infrastructure. Public cloud deployments offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are examples of public cloud providers.
2. Private Cloud:
Private cloud deployments involve hosting services and infrastructure on dedicated resources that are exclusively used by a single organization. The infrastructure can be located on-premises within the organization's data center or hosted by a third-party provider. When compared to public clouds, private clouds provide more security, control, and customization choices. They are appropriate for organisations with strict compliance, security, or performance standards. Private clouds can be managed by the organization's IT team or a managed service provider.
3. Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid cloud deployments combine elements of both public and private clouds, creating a unified environment that allows data and applications to be shared between them. Organizations can utilize public cloud resources for non-sensitive workloads, scalability, or temporary capacity needs, while keeping sensitive or critical workloads and data on a private cloud. The hybrid cloud offers flexibility, allowing organizations to take advantage of the benefits of both public and private clouds. It allows for the seamless integration of on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services.
Cloud Computing Examples:
Cloud computing is widely used across various industries and for a wide range of applications. Here are some examples of how cloud computing is utilized:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
AWS is one of the world's largest and most well-known cloud service companies. It offers a wide range of services including computing power, storage options, content delivery, machine learning, and more.
Microsoft Azure:
Azure is Microsoft's cloud computing platform that provides services for computing, analytics, storage, and networking. It also integrates well with Microsoft's software suite, such as Office 365 and Windows Server.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
GCP offers a suite of cloud computing services, including computing, storage, databases, machine learning, and data analytics. It is known for its strong offerings in data management and analytics.
IBM Cloud:
IBM Cloud provides a range of cloud computing services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS solutions. It also emphasizes enterprise-grade services, including AI, blockchain, and IoT.
Conclusion:
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access, utilize, and manage computing resources. It offers a flexible and scalable approach to computing, allowing users to leverage powerful infrastructure, software, and services without the need for extensive local hardware and infrastructure management. With cloud computing, users can provision resources on-demand, scale them up or down as needed, and pay only for what they use.